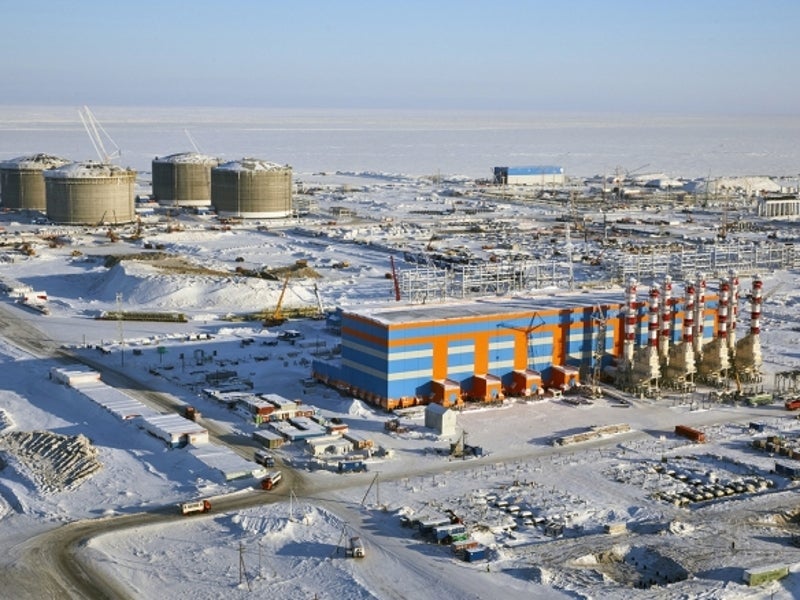
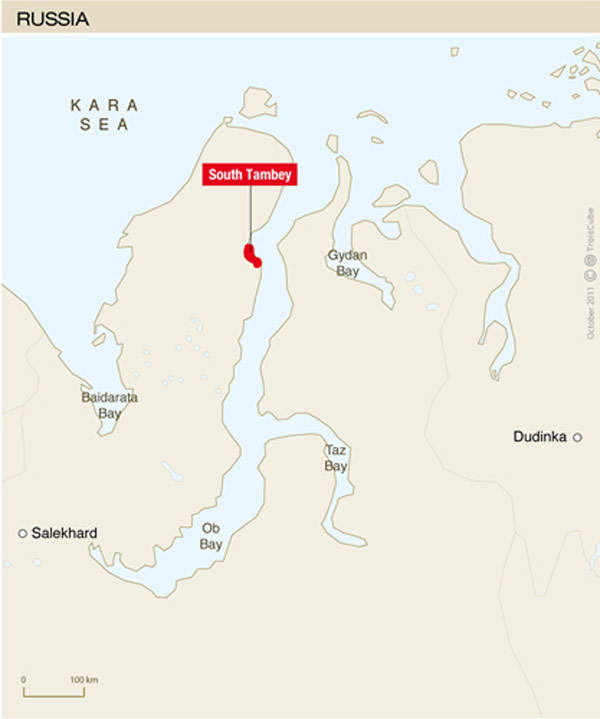
The Yamal liquefied natural gas (LNG) project includes the development of the South Tambey (Tambeyskoye) gas field, located near Sabetta in the Yamal peninsula in Russia.
The Russian Government declared the project to be of national interest. The entire project is expected to cost approximately $27bn.
Novatek is executing the project through its subsidiary Yamal LNG. The company currently holds 50.1% interest in the project, while Total holds the remaining 20% together with CNPC (20%) and Silk Road Fund (9.9%). Total originally became a partner in the project in October 2011.
Novatek signed an agreement with Gazprom for the distribution of LNG produced from the site.
The LNG project will comprise of four processing trains. The first train commenced operations in December 2017, followed by the second in July 2018 and the third in November 2018. The fourth train is expected to come online by 2020.
Challenges associated with the LNG project site geology
Yamal peninsula is currently estimated to hold the largest gas reserves in the world. However, the region is also noted to feature some of the toughest working conditions. The land is boggy, making drilling operations a challenge.
In the winter season, daylight is available only for a short period of time, when the majority of the operations need to be carried out. In addition, the area is very remote with no local workforce available. The nearest potential market is also located 3,000km away.
Due to the extreme climatic conditions in the region, the construction of the LNG project is being carried out in a modular fashion. The erection of the field’s development facilities presents various challenges as a result of the permafrost conditions in the area.
Due to permafrost, the underground layer of soil stays frozen for at least two years. The layer above it freezes and thaws with the change in season.
As a result, infrastructure cannot be allowed to come into contact with this soil in order to ensure stability. The infrastructure is usually erected on stilts in such conditions.
The LNG plant’s liquefaction technology was also carefully chosen to ensure suitability for these conditions.
Despite these challenges, several companies are investing in the region to recover the large gas reserves. Novatek and Total are also developing another project, Shtokman, in the same region.
Reserves of the South Tambey (Tambeyskoye) onshore gas field
The South Tambey field was discovered in 1974. 2D seismic studies were carried out at the field in 2010 in order to understand the geological properties.
South Tambey field contains 72 commercially viable gas layers, including 33 shallow dry gas layers and 28 deeper gas layers. The depth of these layers varies from 900m to 2,850m.
The field’s estimated reserves stand at 44 trillion cubic feet (tcf) of gas and 550 million barrels of condensate, while the proven reserves stand at 1.26tcf of gas and 51.6mt of gas condensate.
The gas field will be capable of producing up to 27bcm of natural gas a year over a period of 20 years. A total of 208 directional production wells are planned to be drilled for the development of the field. Drilling of 126 production wells was completed and four drilling rigs were put into operation by the end of 2018.
Yamal liquefied natural gas (LNG) project infrastructure
Plans outlined for the Yamal LNG project include the construction of an LNG plant, a processing facility for gas and condensate treatment, a gas transmission pipeline and well sites.
A gas gathering system, a seaport at Sabetta, and a fleet of ice-class LNG tankers to transport the LNG are also scheduled for inclusion under the project.
The LNG processing plant has a capacity of 17.4 million metric tonnes a year (Mmtpa) of gas and one million metric tonnes of condensate. It will comprise four LNG trains, as well as storage and loading facilities.
Three of the LNG trains have an individual capacity of 5.5Mmtpa, while the fourth train will have a capacity of 0.9Mmtpa.
The processing plant also comprises four 160,000m³ cryogenic LNG storage tanks, an LPG fractionation facility along with stable gas condensate, and refrigerant storage facilities.
As many as 16 custom-designed Russian arctic classified ARC7 ice-class LNG tankers are operating for the project. The tankers provide assistance in the transportation of LNG to markets in the European, North American and Asia-Pacific regions.
The loading / unloading tankers have a deadweight ranging between 183,000t and 208,000t and a shipping capacity of 172,600m³. They are capable of operating in the harsh climatic conditions of the Yamal peninsula.
Measuring 300m in length, the tankers can sail at a speed of 19.5kts in open water and at 5.5kts in 1.5m-thick ice.
The first LNG carrier for transporting LNG produced from the project was named Christophe de Margeri and commissioned in March 2017. Ten LNG carriers have been operational since 2018, while commissioning of the remaining is expected to take place in 2019.
A power plant with a designed capacity of 376MW was also constructed to support the LNG plant’s operations.
The shipping infrastructure of the project includes an LNG and gas condensate offloading jetty installed with two tanker loading berths, rolling cargo berths, material offloading facilities and port fleet berthing facilities at the port of Sabetta. The port harbour is protected by a 2km-long ice barrier.
Financing for the Yamal LNG project
The Yamal LNG project was financed by the National Welfare Fund of Russia, Sberbank, Gazprombank, China Development Bank, the Export-Import Bank of China, and Japan Bank for International Cooperation (JBIC) along with various European banks including Raiffeisen Bank International and Intesa Sanpaolo.
Insurance coverage for the project was provided by various European agencies including SACE, Euler Hermes, COFACE and EKN.
Contractors for the Russian ‘national interest’ onshore gas project
The engineering, procurement and construction (EPC) activities for the project are being carried out by the consortium of Technip, Chiyoda and JGC under a contract awarded in April 2013.
Chicago Bridge and Iron Lummus (CBI Lummus) was contracted to carry out the pre-FEED and FEED studies for the project.
GE is supplying a total of six Frame 7E gas turbines, 18 centrifugal compressors, six variable speed drives and six waste heat recovery units (WHRUs) for the LNG trains as part of a contract valued at approximately $600m.
The company is also providing installation supervision and support during the project’s commissioning stage.
Novatek awarded a contract to Daewoo Shipbuilding & Marine Engineering in July 2013 for the construction and delivery of total 16 ARC7 ice-class LNG carriers.
Aker Arctic provided the outline design in addition to evaluation of vessel performance of the ice-breaking LNG carriers used for the LNG project.
VINCI was contracted to supply four cryogenic LNG storage tanks for the project in January 2014.
Atomflot was awarded a contract by Novatek for providing the long-term port fleet services related to tug and icebreaker assistance at the Port of Sabetta in November 2014.
Vyborg Shipyard was subcontracted by Atomflot in April 2015 for a 10MW diesel-powered harbour icebreaker. Technopromexport was contracted to construct the power plant, while Siemens was contracted to provide eight SGT-800 industrial gas turbines.
Related content
Nagarjuna Oil Corporation’s Cuddalore Refinery, Tamil Nadu, India
Nagarjuna Oil Corporation Limited (NOCL) is developing a state-of-the-art crude oil refinery in Cuddalore in the southern Indian state of Tamil Nadu.
Dangerous fossil fuels: Q&A with Enel head of safety Alda Paola Baldi
When talking about safety at energy-producing power plants, many think primarily about the safety at nuclear plants – especially after recent painful memories of the Fukushima disaster in March 2011.