The Gimboa field lies in block 4/05, approximately 85km off the Angola coast, in 700m (2,296ft) of water. The field is operated by Sonangol on behalf of Norsk Hydro, ACR (Angola Consulting Resources) and SOMOIL (Sociedade Petrolefira Angolana). Recoverable reserves have been put at 50 million barels of oil equivalent.
The Gimboa project is based on three production and four water injection subsea wells, which are clustered around a central manifold. This is tied back to a floating production, storage and offloading unit (FPSO).
Technip was awarded the contract, worth approximately $70m, for the engineering, procurement, fabrication, testing, installation and pre-commissioning of one production flowline, one water injection flexible flowline, one gas lift flexible pipe, one service umbilical, an associated flexible risers system and flexible well jumpers.
The engineering was carried out with the assistance of its operations and engineering centre in Luanda, while the company’s umbilical plant, Angoflex, manufactured the umbilical and provided logistic support.
The flexible lines were manufactured by Flexi France in Le Trait (France). This contract also included the installation of other subsea equipment, provided by Sonangol P&P. Offshore operations were performed using a dynamically positioned vessel in 2008.
Gimboa field came online in April 2009.
Gimboa field FPSO
The contract to provide and manage the FPSO was awarded to Saipem in a six-year $570m contract with a five-year extension option. Delivery to the Gimboa field was concluded in 2008.
Saipem converted the oil tanker T/T Magdelaine into the FPSO Gimboa. The FPSO has 1.8 million barrels of oil storage and a production capacity of 60,000bpd.
The tanker was built by IHI in Kure, Japan, in 1977, and was converted in Dubai DryDocks. The hull has an overall length of 337m, a 54.5m breadth and a 27m moulded depth.
Its loaded draught is 21m and it has a deadweight of 273,777t. It is powered by steam turbine boilers with an output of 87,000kg/hr which gives the vessel a transit speed of 10kt (14kt before conversion). Power is from two steam turbine-driven generators with an output of 14MW each.
The FPSO Gimboa has 100 berths and an operating crew of 50. The mooring is carried out by a 12-leg spread system consisting of polyester / chain anchored by suction piles.
Gimboa field contractors
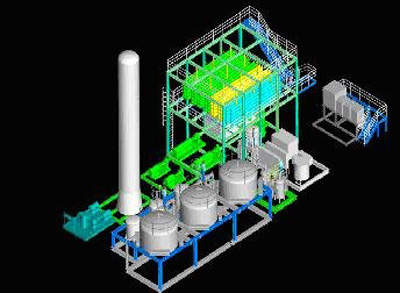
Saipem subcontracted the fabrication company Lamprell to build six topside process modules in a $30.3m deal. In addition to the main contract, this included an option for the fabrication of the piperack worth another $8.7m.
These modules are for lift and flash gas compression, high and low-pressure separation, plus a chemical injection skid, a processing manifold and an equipment room.
VWS Westgarth supplied the sulphate removal package. Its scope consists of a water injection plant in a single lift module arrangement comprising of: seawater coarse strainers, a chlorination unit, dual media fine filtration, guard cartridge filters, HP feed pumps, a sulphate removal membrane system, a fresh water membrane system, a vacuum deaerator, water injection pumps, a chemical cleaning system, chemical dosing systems, control valves and instrumentation, fresh water distribution systems, module lighting, fire and gas detection and fire-fighting systems.
Processing facilities at the west African, Angola field
The processing facilities give the FPSO a maximum production of 60,000bpd of oil and 60,000bpd of water. Maximum gas production is 36.8 million cubic feet a day.
There is a low and high-pressure ignition-type continuous gas flare of 1.49 million cubic metres a day but that can be raised to a maximum of 87 3.14 million cubic metres a day in an emergency.
The gas compression facilities are rated at 20 million scfd. The tanker can store 1,800,000 barrels of crude in the tanks. There are also slop tanks able to hold 108,000 barrels.