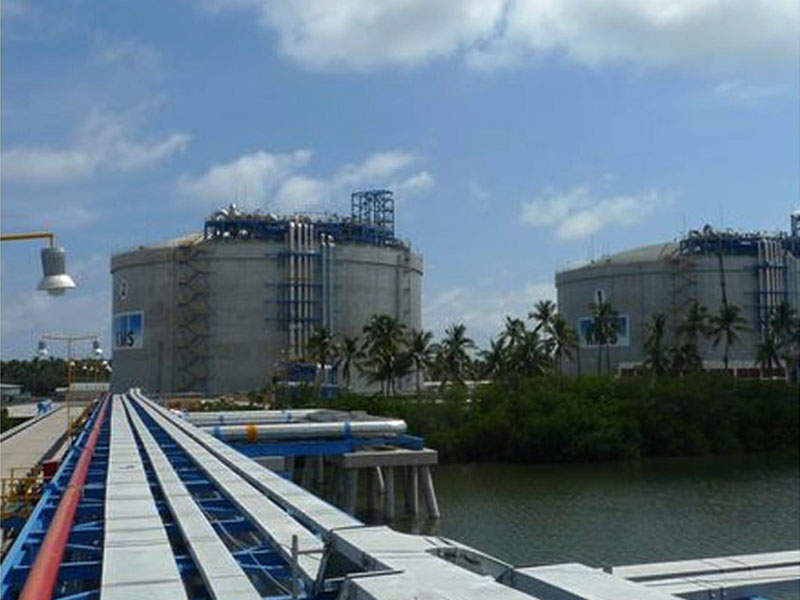

Construction of the first liquefied natural gas (LNG) receiving and regasification terminal in the Middle East is currently underway in the Hidd Industrial area of Kingdom of Bahrain.
The new facility is intended to help Bahrain meet the increasing demand for gas supplies for industrial and urban development.
The terminal is being developed and will be operated by a joint venture (JV) known as Bahrain LNG WLL, which is owned by Bahrain’s National Oil & Gas Authority (NOGA, 30%), Teekay LNG (30%), Samsung C&T (20%) and the Gulf Investment Corporation (GIC, 20%).
It is being developed on build-own-operate-transfer (BOOT) basis over a 20-year period beginning in July 2018, and will be handed over to the Government of Bahrain at the end of the BOOT period.
The project’s environmental impact assessment (EIA) was conducted in 2014 and was accepted by the Supreme Council for Environment in September 2015. The EIA’s validity was re-confirmed by the Supreme Council for Environment in March 2016.
Bahrain LNG terminal location and infrastructure
The LNG terminal is being constructed at an offshore location 4.3km away from the existing breakwater at the Khalifa Bin Salman Port (KBSP). It will have a production capacity of 800 million standard cubic feet a day.
Plans for the site include an offshore jetty and breakwater to receive LNG shipments, as well as a floating storage unit (FSU) and a regasification platform. It will be linked to underwater and surface gas pipelines from the platform to shore.
Onshore infrastructure will include a gas receiving plant and a nitrogen production facility.
Bahrain LNG terminal construction
The LNG terminal construction began in the second week of January 2017 and is expected to be completed in approximately 32 months.
The construction works include breakwater, dredging activities, and the ground piling works for the LNG jetty and associated platform.
Marine transportation activities between KBSP and the LNG terminal are set to continue with minimal disruption throughout the construction phase.
Financing
The terminal is estimated to be funded by an investment of $741m, which will be financed via a public-private partnership (PPP), including a combination of equity capital and project finance through a consortium of both regional and international banks.
Organisations that have agreed to provide financial support include the Standard Chartered Bank, Arab Petroleum Investments Corp (APICORP), and the Korea Development Bank.
Other banks such as the Ahli United Bank, Santander, Crédit Agricole, ING Bank, Natixis, and Société Générale are also confirmed to be contributing funds.
The project achieved financial closure in December 2016. Korea Trade Insurance Corp (K-SURE) agreed to provide commercial and political risk cover for approximately 80% of the financing arrangement.
PFI Awards recognised the Bahrain LNG project financing deal as the Middle East Deal of the Year for 2016.
Contractors involved with Bahrain LNG terminal
GS Engineering & Construction was awarded a $652m engineering, procurement and construction (EPC) contract for the development project in December 2015.
Six Construct, Oceanus, MCSC, and GPS were subsequently appointed by GS Engineering & Construction as subcontractors.
Teekay LNG will supply a floating storage unit (FSU) by converting a 174,000m³ LNG carrier from Daewoo Shipbuilding & Marine Engineering (DSME).
WorleyParsons was selected to perform environmental impact assessments (EIA) for the facility in 2014.



