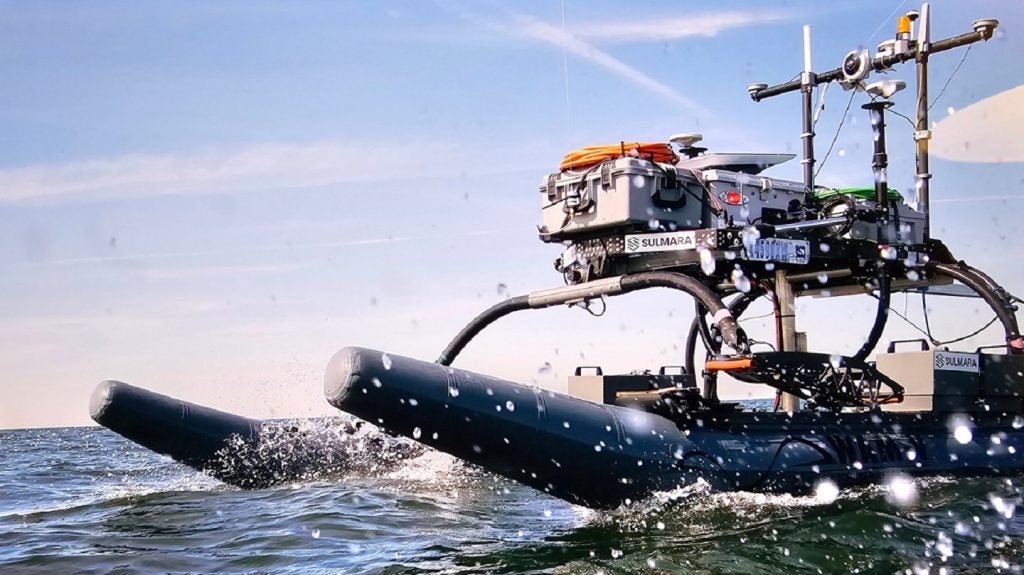
Sulmara has completed a high-resolution geophysical survey for Bayou Bend CCS, a carbon capture and storage (CCS) project in south-east Texas, US.
Sulmara’s survey produced what it describes as the "best data we’ve seen" from a USV at the Bayou Bend project.
It employed an electric WAM-V 16 USV for offshore data acquisition to lower the carbon footprint of the survey and shorten the survey duration.
Bayou Bend CCS selected Sulmara to undertake an archaeological and geohazard assessment along the proposed pipeline route from landfall to the future offshore platform locations.
Furthermore, the collaboration between Bayou Bend CCS and Sulmara leveraged the Starlink satellite system, backed by SpaceX, to maintain good communications between the shore team and the USV.
Sulmara project manager Darius Rivera said: “With the survey area around 15km from shore, we integrated the WAM-V with Starlink to achieve higher-speed communications with the mobile remote command centre.
“This is the first time we have been able to go beyond the 3km mark with this size USV, ensuring improved quality of data and reducing the time needed to collect the information when compared to a conventional survey vessel.”
Nearly 100,000 gross acres of Bayou Bend’s total acreage are located on land in the Texas counties of Chambers and Jefferson, and around 40,000 gross acres offshore between Beaumont and Port Arthur.
Bayou Bend CCS has nearly 140,000 gross acres of pore space for permanent CO₂ sequestration. It has gross storage capacity of more than one billion metric tonnes.
Last year, Equinor acquired a 25% stake in Bayou Bend CCS. Other partners in the project include Chevron (50%) and Talos Energy (25%).