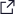Robotics is the branch of technology that deals with the design, construction, operation, and application of robots. The oil and gas industry has emerged as a significant adopter of robotic technology, with its applications continuously evolving.
Robots equipped with advanced technologies are yielding increasingly positive results in improving safety and efficiency within oil and gas operations.
They are proving invaluable for executing complex tasks at production facilities, thereby protecting workers from hazardous environments, improving health, safety, and environment (HS&E), and reducing the likelihood of costly shutdowns.
As a result, companies such as Equinor, TotalEnergies, and Shell are deploying them to work alongside humans on offshore sites. Their ability to perform repetitive and mundane tasks with minimal errors is saving time and internal resources for companies.
Furthermore, it allows them to deploy field technicians on more critical issues.
Oil and gas operations are labour-intensive and involve numerous repetitive tasks, many of which occur in hazardous environments and face various obstacles.
As a result, robotics presents an excellent solution to many challenges within the industry, as robots can handle more strenuous tasks and complex procedures more effectively than humans.
They provide greater reliability and efficiency in completing assigned tasks while also enhancing operational safety. The integration of terrestrial, aerial, and underwater robots is already playing a crucial role in several high-stakes oil and gas projects throughout the value chain.
Robots can access hard-to-reach areas, carry out tasks beyond human capabilities, and operate continuously without needing breaks. Hence, they are being utilised as effective solutions for conducting inspections in difficult or hazardous environments, thereby avoiding human exposure to such sites.
Lately, cleaning of storage tanks is emerging as another prominent use case for robotics with companies such as Saudi Aramco, Woodside, SK Innovation, and IndianOil, exploring the potential of robotic crawlers in this application.
Additionally, there is an increase in collaboration between oil and gas companies and technology vendors, enabling the diversification of robotic use cases with the integration of AI, Internet of Things, cloud, and edge computing.
Current robots used in oil and gas operations include terrestrial crawlers, quadrupeds, aerial drones, and autonomous underwater vehicles, along with an increasing number of industrial robots and collaborative robots capable of performing complex tasks.
These developments are anticipated to drive future growth in robotics within the oil and gas sector, reducing risks to human workers who operate alongside heavy machinery in often remote and challenging environments.
Further details of oil and gas companies and their adoption of robotics can be found in leading data and analytics company GlobalData’s new theme report, Robotics in Oil and Gas.