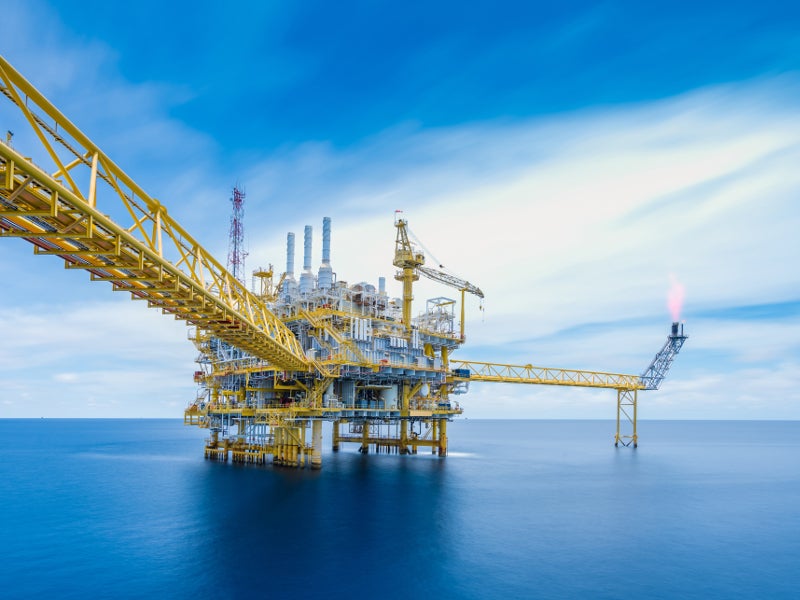
The Kasawari gas field is located in the South China Sea, offshore Sarawak, in Malaysia. It is being developed by Malaysian oil and gas company Petronas.
The field is estimated to contain 3.2 trillion cubic feet (tcf) of natural gas resources. It is expected to produce 900 million standard cubic feet per day (mmscfd) of gas and 3.5 million barrels of condensate per day.
The Kasawari gas field is expected to commence production in 2023.
Petronas also reached a final investment decision (FID) for the development of the Kasawari carbon capture and storage (CCS) project in November 2022.
The CCS project is expected to capture up to 3.3 million tons (Mt) of carbon dioxide equivalent emitted by flaring at the gas field each year.
Kasawari gas field location
The Kasawari gas field is located at a water depth of approximately 108m in block SK316 in Central Luconia Province, Malaysia.
The field is situated approximately 200km away from the coast of Bintulu, Sarawak.
Block SK316 in the Sarawak region also holds the NC3 and NC8 fields.
Kasawari field discovery and reserves
The Kasawari gas field was discovered by Petronas in November 2011. Block SK316 hosts large-scale proven gas discoveries and exploration prospects with comparatively high levels of carbon dioxide content.
Development of the field involves the usage of advanced technologies to address the issue of high CO₂ levels during production.
Kasawari gas field development plan
The Kasawari gas field development will comprise an 8,600t KSDP-A drilling platform with nine slots, 47,000t eight-legged central processing platform (KSCPP) and Sarawak riser platform (SKR-D). Other components will include an 85km-long export pipeline connecting to an E11R-A platform, inter-platform bridges linking the CPP to the KSDP-A, and a flare tripod.
The full well stream (FWS) produced from the drilling wells will be transported to the KSCPP using a 100m bridge-linked piping system. The KSCPP will separate water, condensate and gas.
Gas and condensate from the KSCPP will be transported back to the SKR-D collector platform through an 80km-long pipeline. From there, it will be sent to onshore facilities.
The gas produced will be processed to remove H₂S and CO₂ and will undergo dehydration offshore before reaching the SKR-D platform.
Wastewater accumulated during the separation process will be treated up to an oil content of 30mg/l and released into the sea.
Kasawari gas development details
The gas project is being developed in four phases, which will include an installation phase, pre-commissioning and commissioning phase, operations phase, and project decommissioning phase.
The pre-commissioning works will include cleaning, gauging and hydro-testing prior to the commissioning of pipelines.
The offshore installation works will include the transportation of materials and components, and the installation of the platform, flare tripod and bridge-link. This phase will also include the installation of pipelines and hook up to facilities.
The first steel cut ceremony for the Kasawari offshore platform took place in January 2020. The wellhead platform jacket and topsides reached the project site for installation in 2021.
Phase two of the project’s development will involve the construction and installation of a new fixed platform connecting the phase one central processing platform.
The compressed carbon dioxide from the new platform will be reinjected into the depleted reservoir at the M1 Field using a 138km-long, 16-inch subsea pipeline.
Gas export from Kasawari field
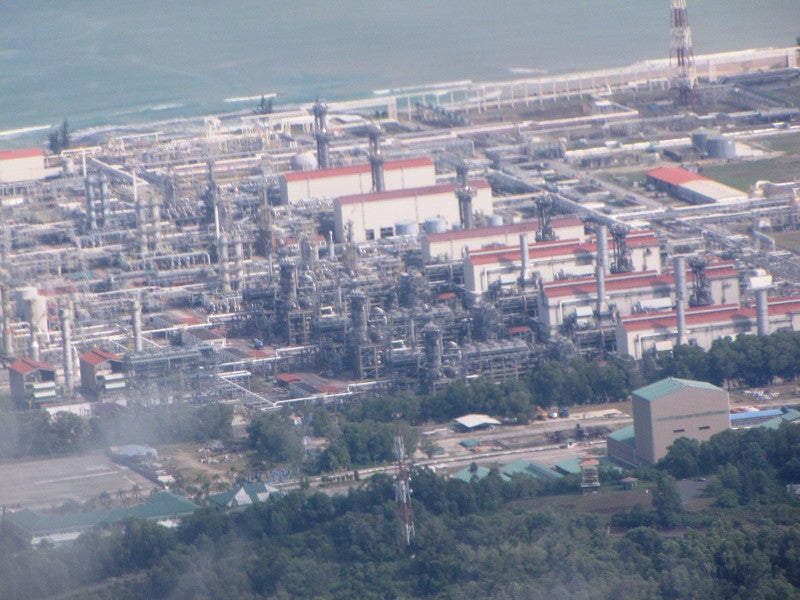
The Kasawari field, along with the NC3 and NC8 fields, will supply gas to the ninth train of the existing LNG terminal owned by PL9SB, a subsidiary of Petronas.
The ninth LNG liquefaction train is located in the Petronas LNG Complex in Bintulu, Sarawak. Commissioned in 2017, the train has a production capacity of 3.6 million tons per annum (mtpa).
Petronas will supply up to 1.2mtpa for a period of 15 years under the LNG sale and purchase agreement signed with Thailand’s PTT Public Company.
Contractors involved in Kasawari gas development project
Honeywell UOP was selected to provide its modular natural gas processing technology for the project’s offshore gas purification plant in July 2020.
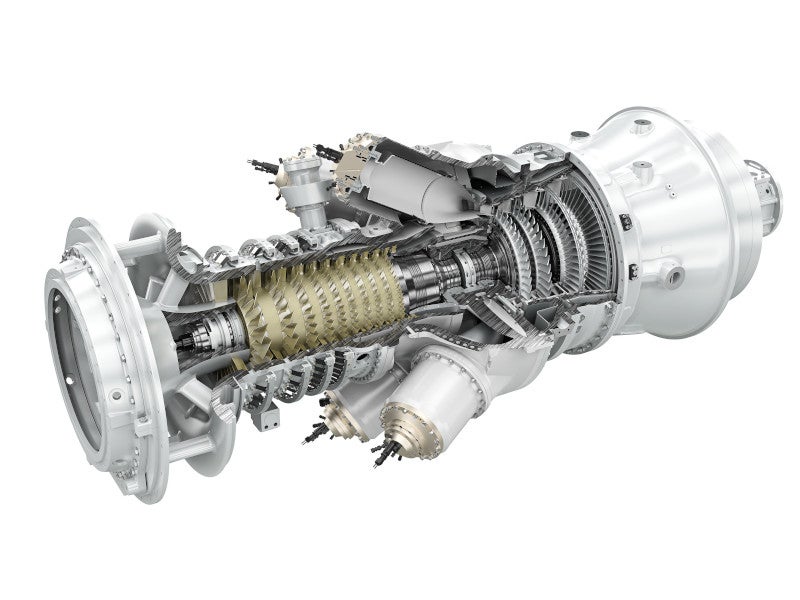
Siemens Energy was contracted to provide three SGT-300 industrial gas turbine generators, three mechanical-drive SGT-300 gas turbines and three DATUM centrifugal compressors for the project in June 2020.
Van Leeuwen Malaysia received a contract to provide steel pipes, duplex pipes, and carbon steel fittings and flanges for the project in 2020.
Wasco Energy provided asphalt enamel, concrete weight coatings and anodes for pipes used in the project.
MMC Oil & Gas Engineering (MMCOG) was contracted to provide engineering design services for the facilities.
In October 2019, Malaysia Marine and Heavy Engineering (MMHE) in consortium with Technip Energies was contracted by PETRONAS Carigali to deliver engineering, procurement, construction, installation and commissioning (EPCIC) services for the project.
White Quest Synergy was contracted to design safety case and performance standards for the Front-End Engineering Design (FEED) project, while Golden Ecosystem was appointed as the environmental impact assessment (EIA) consultant to conduct the environmental study.
Contracts awarded for the Kasawari CCS project
MMHE was awarded the EPCIC contract for the Kasawari CCS project in February 2022.
Baker Hughes was contracted to supply two trains of low-pressure booster compressors for the CCS project in January 2023.