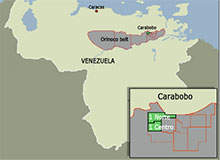

Carabobo is a massive oil project being developed in Venezuela. The onshore oil field development comprises seven production blocks on the eastern part of the Orinoco Belt which is believed to contain approximately 513 billion barrels of heavy crude oil.
Venezuela’s state-owned Petroleos De Venezuela (PDVSA) is developing the huge oil field under a three multibillion dollar development projects namely Carabobo-1, Carabobo-2 and Carabobo-3 by forming three separate joint ventures with foreign partners.
Carabobo 1, the fourth biggest onshore oil field in the world, containing 31 billion barrels of recoverable oil reserve, started production by the end of 2012. Carabobo-2 and Carabobo-3 are yet to commence production.
Development partners for the Carabobo onshore oil project
The Carabobo-1 project is owned and operated by Petrocarabobo, a joint venture formed between PDVSA (60%), Repsol (11%), Petronas (11%), ONGC Videsh (11%), Indian Oil Corporation (3.5%) and Oil India (3.5%) in May 2010. Petronas, however, announced its withdrawal from the project in September 2013.
The Carabobo-2 project is owned and operated by Petrovictoria, a joint venture of PDVSA (60%) and Rosneft (40%), which was officially formed in May 2013.
The Hamaca ‘heavy crude’ upgrade project is one of the four projects exploiting the Venezuelan extra-heavy crude oil and bitumen deposits situated in the Orinoco heavy-oil belt, in Central Venezuela.
The Carabobo-3 project is owned and operated by Petroindependencia, a joint venture comprised of PDVSA (60%), Chevron Corporation (34%), Suelopetrol (1%) and Carabobo UK (JCU) – a joint venture between Mitsubishi, Japan Oil, Gas and Metal National Corporation (JOGMEC) and Inpex (5%). The joint venture was formed in May 2010.
Details of Carabobo-1, 2 and 3 projects
The Carabobo-1 project involves the development of two production blocks namely Carabobo-1 Norte and Carabobo-1 Centro. The Carabobo-2 project also comprises two blocks, namely Carabobo-2 North and Carabobo-4 West. The Carabobo-3 project consists of three blocks namely Carabobo-2 Sur, Carabobo-3 Norte and Carabobo-5. The combined recoverable oil reserves under the three projects are estimated to be more than 100 billion barrels.
Carabobo-1 is the most advanced among the three projects. It produced its first oil from the well CGO-0005 in December 2012. Carabobo-1 was producing 30,000 barrels of crude oil per day towards the end of 2013. More than 40 additional development wells are planned to be drilled at the field using two drilling rigs. The oil field is expected to produce about 400,000 barrels of oil per day by 2018.
Carabobo-2 was in very early stage of development as of the beginning of 2014.
Conceptual engineering for the potential development of the Carabobo-3 oil field was underway by the end of 2013. The oil field is planned to have an early production level of 50,000 barrels per day, which is scheduled to peak at 400,000 barrels per day in 2020.
Each of the three projects will have an upgrader facility capable of processing 200,000 barrels of heavy crude oil into lighter synthetic oil per day. The upgraders for Carabobo-1 and Carabobo-2 are expected to be built by 2017.
The oil produced from the Carabobo project is planned to be transported by trucks until a trunk pipeline is constructed by PDVSA for carrying the Carabobo oil to the Port of Araya for export.
Contractors involved with the Carabobo-1 oil project
Technip was awarded the contract for the front-end engineering design (FEED) and the first phase project management consultancy services for the Carabobo-1 upgrader project in April 2012.
Technip is executing the contract from its operating centre in Rome in collaboration with PDVSA – Ingenieria y Construccion, a subsidiary of PDVSA.